Abstract
With the development of various strategies of anti-CD19 immunotherapy for treatment of B cell malignancies, it remains to be elucidated whether CD19 targeting with a monoclonal antibody impairs subsequent CD19 targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CART19) therapy. In this study, we evaluated the potential interference between the CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody tafasitamab and CART19 treatment (using a construct similar to the FDA approved therapy, FMC63-41BBζ, tisagenlecleucel) in preclinical lymphoma and leukemia models.
For in vitro assays, the CD19 + cell lines JeKo-1 (mantle cell lymphoma), Nalm6 (acute lymphoblastic leukemia), and OCI-Ly7 (diffuse large B cell lymphoma) were used. When CART19 were co-cultured with CD19 + tumor cells in the presence of increasing concentrations of tafasitamab (10-400 µg/mL) or the isotype control, an impairment of CART19 functions at the highest concentration of tafasitamab was observed. However, when tafasitamab was cocultured with tumor cells overnight and removed from the culture by washing, there was no impairment of CART19 anti-tumor activity or effector functions compared to a pre-culture with isotype control.
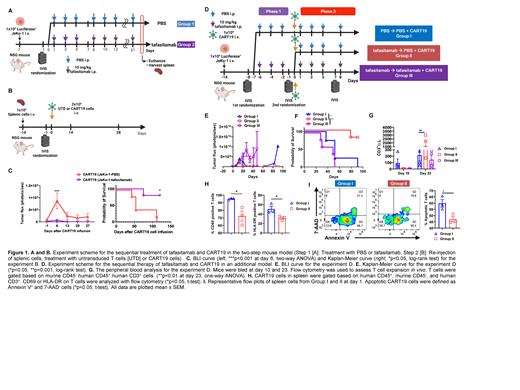
We then aimed to validate these findings in xenograft mouse models by determining whether prior tafasitamab treatment impairs subsequent CART cell function. First, a two-step JeKo-1 xenograft model was created through inoculation of 1x10 6 luciferase + JeKo-1 cells to immunocompromised NOD-SCID-γ -/- (NSG) mice via tail vein injection. One week later, tumor burden was assessed by bioluminescence imaging (BLI) and mice were randomized to receive either 1) PBS (Group 1) or 2) 10 mg/kg of tafasitamab (Group 2) (Fig. 1A). Treatment was performed until the mice reached the endpoint due to the high tumor load. When reaching the endpoint, mice were euthanized and spleen was harvested. Splenic cells were then injected to naïve NSG mice. Two weeks after the inoculation of splenic cells (PBS or tafasitamab treated), mice were imaged with BLI and randomized according to their tumor burden to receive 2x10 6 of 1) untransduced T cells (UTD) or 2) CART19 (i.v.) (Fig. 1B). Mice, treated with CART19 demonstrated potent anti-tumor effects and showed prolonged survival compared to UTD control mice. Interestingly, CART19-treated mice inoculated with Group 2 splenic cells (pretreated with tafasitamab) showed a significantly better tumor control and overall survival compared with mice engrafted Group 1 splenic cells (PBS pretreatment) (Fig. 1C).
This finding led us to further investigate the effects of prior tafasitamab therapy on subsequent CART19 treatment. In this context, we studied the sequential treatment with tafasitamab and CART19 in an additional JeKo-1 xenograft model (Fig. 1D). In brief, NSG mice were inoculated with luciferase + JeKo-1 on day -14. On day -8, mice were imaged and randomized to the PBS (Group I) or tafasitamab (10 mg/kg) group. On day -1 tafasitamab treated mice were imaged again, randomized to the tafasitamab discontinuation (Group II) or continuation (Group III). Treatment with PBS was continued in Group I. All groups were administered with 1x10 6 of CART19 on day 0. Cotreatment of JeKo-1 xenografts with tafasitamab and CART19 led to impaired anti-tumor activity presumably as a result of CD19 binding competition between tafasitamab and CART19 (Group III). Mice treated with tafasitamab followed by CART19 had improved tumor control compared to mice treated with PBS followed by CART19 (Fig. 1E-F). Serial peripheral blood analysis demonstrated that mice from Group I showed the highest CART19 expansion on day 10. Strikingly, Group II exhibited weak CART19 expansion at day 10, but strongest expansion on day 23 (Fig. 1G). We therefore hypothesized that prior treatment with tafasitamab results in modulation of CART19 cell activation. To test this hypothesis, spleens of satellite mice were harvested 24 hours after CART19 administration. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that the mice from Group II showed significantly lower CD69 and HLA-DR expression on CART19 cells compared with Group I, and reduced apoptosis as measured by the Annexin assay (Fig. 1H-I).
In summary, concomitant treatment of tafasitamab and CART19 led to impaired anti-tumor activity while, in contrast, sequential treatment of tafasitamab and CART19 did not inhibit CART19 anti-tumor activity but rather promoted anti-tumor effects in xenograft models.
Sakemura: Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Augsberger: MorphoSys AG: Current Employment. Schanzer: MorphoSys AG: Current Employment. Patra-Kneuer: MorphoSys AG: Current Employment. Heitmüller: MorphoSys AG: Current Employment. Steidl: MorphoSys AG: Current Employment. Endell: MorphoSys AG: Current Employment. Ding: DTRM: Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Parikh: Pharmacyclics, MorphoSys, Janssen, AstraZeneca, TG Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, AbbVie, and Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Verastem Oncology, and AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kay: Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Targeted Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CytomX Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding. Nowakowski: Celgene, NanoString Technologies, MorphoSys: Research Funding; Celgene, MorphoSys, Genentech, Selvita, Debiopharm Group, Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cox: Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Kenderian: Humanigen, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal